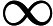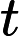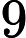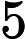在 Aurelien Geron 的书中,我发现了这一行
This cost function makes sense because –log(t) grows very large when t approaches
0, so the cost will be large if the model estimates a probability close to 0 for a positive instance, and it will also be very large if the model estimates a probability close to 1
for a negative instance. On the other hand, – log(t) is close to 0 when t is close to 1, so
the cost will be close to 0 if the estimated probability is close to 0 for a negative
instance or close to 1 for a positive instance, which is precisely what we want.
我没有得到的是,如果模型估计正实例的概率接近 0,成本会很大,如果模型估计负实例的概率接近 1,成本也会很大?