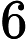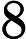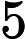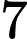检查你的尝试
由于您正在尝试自学 C,因此让我们实际向您展示代码中存在哪些问题,并展示如何利用 C 的完整功能正确解决此问题。
#include <stdio.h>
以下声明无用
int primearray(int,int);
下面的声明应符合 ANSI
main()
主函数()
{
您不应该将这么大的数组用作堆栈变量,实际上要么将其声明为全局变量,要么动态分配它(更好的解决方案)
int alpha, k, j, i=1, prime[200000], count = 0;
prime[0]=2;
/* Define number which counts number of primes in interval [0,alpha] */
int totprime=1;
您应该将代码分成单独的函数,以便您可以简单轻松地处理每个部分
例如一个函数,它接受一个数字并使用任何方法找到所有素数,这样你就可以从一个简单的函数开始,当你学习更好的方法时,你实际上可以使这个例程更快。
printf("Enter the number of which you want the prime factorization\n");
scanf("%d",&alpha);
/* This procedure makes a list of all prime numbers up to alpha */
下面的块有很多问题。
首先它是次优的,因为它测试了太多的素数。
对素数的测试是不正确的,并且不会导致值总是等于 j,而应该是。此外,它非常占用 CPU,您可以使用模运算符更有效地获得结果
存储素数的测试很奇怪。
这整个块应该在它自己的功能中。
for (j=3 ; j<alpha ; j++)
{
for (k=0 ; k<i ; k++)
{
if ((j/prime[k])*prime[k]==j)
break;
else
count = count + 1;
}
if (count == i)
{
prime[i]=j;
i = i + 1;
count = 0;
totprime = totprime + 1;
}
else
count = 0;
}
不要评论明显的代码代码显示您将打印素数添加评论是轻浮的并且有损
/* Print prime numbers */
printf("The primes are:\n");
for (j=0 ; j<totprime ; j++) printf("%d\n",prime[j]);
像上面那样使用 for 循环是不好的形式,你不应该在同一行使用 printf 语句。
一般来说:当你编码时,你的标签和块样式不一致你应该使用一致的方式来标记你的块代码的阅读频率远高于使用一致的样式编写有助于遵循逻辑
printf("Total number of primes: %d\n",totprime);
C 不支持动态数组。下面的代码不是标准的。如果您的平台/编译器支持它,您在移植代码时会得到不一致的结果。
int primefac[totprime];
下面的块有很多问题。
for (j=0 ; j<totprime ; j++)
{
这个测试会失败,因为你假设整数除法是如何工作的(以及它是否会导致分数)更不用说这是一个非常昂贵的操作
if ( (alpha/prime[j])*prime[j] == alpha)
{
primefac[count] = prime[j];
count = count + 1;
}
任何逻辑都完全不需要下面的 else
else
continue;
}
printf("Primefactors are\n");
和上面一样的问题
for (j=0 ; j<count ; j++) printf("%d\n",primefac[j]);
这应该与主要功能一致}
/* 仍在编辑 */ 正确的方法即将出现。
好的,现在让我们弄清楚如何正确解决这个问题。
简单说明问题
您想找到 600851475143 的最大素数。
也就是说你要找到N的最大值
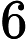


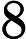
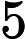


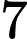
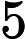













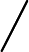












在 C 中,模运算符 (%)(实际上是余数运算符)提供了必要的功能。
那么我们如何做到这一点,首先让我们创建一个函数来做到这一点。我们知道如果 $ a \times b \equiv N \; \forall {a, b} \in \mathbb{Z}^+ $ 然后 $ a \leq \sqrt{N} $ 或 $ b \leq \sqrt{N} $










 then either
then either 




 or
or 





因此,一个简单(粗略)的算法将是查看是否存在一个素数 $p$,使得:$\left。p \leq \sqrt{600851475143} \; \大| \; p \, \vert \, 600851475143 \对。$ such that:
such that: 

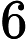


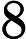
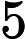


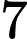
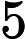

















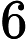


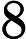
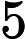


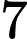
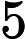



正确的做法
我不会为您提供解决方案,但会引导您了解一些基本概念。
首先,将事物分成更小的块并将每个块视为一个函数是一个好主意。如果你一步一步定义你的方法,那么一个好的经验法则是每一步创建一个函数。如果这是一个复杂的步骤,具有更简单的子步骤,那么该功能应该分为多个子功能。你可能第一次就做错了,没关系,随着你对事情应该如何划分的进行,你会发展出更好的判断力。
好的,让我们使用我们使用流程图的简单算法逐步查看问题

现在基本上上面流程图中的每个框都指向您的主要功能的语句:
/**
* name: primes_upto
* parameters:
* M: finds all primes until M and stores them in zero-terminated list
* list: the pointer to an array of ints
* if list is NULL then it will allocate enough memory
* to store the primes + 1
* if list is not NULL it will truncate insert a 0 at
* the index where value of prime is > M
*
* return value: returns number of primes on success or 0 on failure
*/
int primes_upto(int k, int **list);
int main() {
const int original_N = 600851475143;
int N, a, S;
int *L = NULL; /* list of primes we need to fill */
int *ap = NULL; /* a memory pointer to integers that will point to the next prime */
N = original_N;
do {
S = sqrt(N); /* we have to provide this */
primes_upto(S, &L); /* we have to provide this function */
/* we will make sure that the primes_upto function
injects a zero at the end of the list. Since zero is not a prime
we can use it as a marker to indicate the end of the list
and that way we don't have to worry about how long the list is. */
for (ap = L; ap && *ap != 0; ap++) {
int a = *ap;
if (N % a == 0) {
N = N / a;
break;
}
}
} while (ap && *ap != 0);
printf ("The largest number that divides %d is %u\n", original_N, N);
}